The Interprofessional Experiential Center for Enduring Learning (iEXCEL) is a bold, visionary initiative at the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) designed to transform health care education
Through iEXCEL, learners acquire knowledge, and experience hands-on training in a wide range of realistic but simulated healthcare environments. Using a wide range of simulation technologies they can practise and become proficient in procedural and professional skills before encountering real-life patient care situations.
Opening early in 2018, a new five-level, 192,000 sq ft building, the Davis Global Center, will become home to iEXCEL.
AVI-SPL was selected as the technology integrator for the project. In the world of health care education, AVI-SPL is a leader in installing emerging simulation technologies from advanced human patient simulators and task trainers, to augmented, virtual and immersive reality, as well as the MultiTaction iWall.
We spoke with Bill Schmidt, AVI-SPL Sales Director and Visualization Advocate, and Dr. Pamela Boyers, Associate Vice Chancellor for Clinical Simulation, iEXCEL.
The challenge
The way healthcare education is currently delivered has remained largely unchanged for over a century. Most health care facilities around the U.S. still take a predominantly didactic approach with students learning in traditional classroom settings. This involves listening to lectures, taking notes, and studying for the exam. This is not how the millennials generation prefers to learn and there is growing realization that the traditional approach does not sufficiently prepare students to function at a high level in busy and stressful healthcare environments immediately upon graduation.
While the overall mission of iEXCEL has everything to do with enhancing the outcomes of training and patient care, an important aspect of the vision is to provide digital learning experiences that encourage
students to interact, engage in critical thinking and be guided through competency based learning experiences.
“We are changing the paradigm of how we teach,” says Boyers, “When providing care it is necessary to be very active and engaged with patients and their families. Beyond conducting procedural skills, you must have excellent critical thinking and communication skills and work well in teams. It is very hard to learn this range of skills from books, lectures and PowerPoints.”
WE WANT TO PROVIDE HIGHLY ENGAGING LEARNING EXPERIENCES THAT BETTER SUIT THE WAY THE LEARNERS OF TODAY ABSORB AND APPLY INFORMATION.
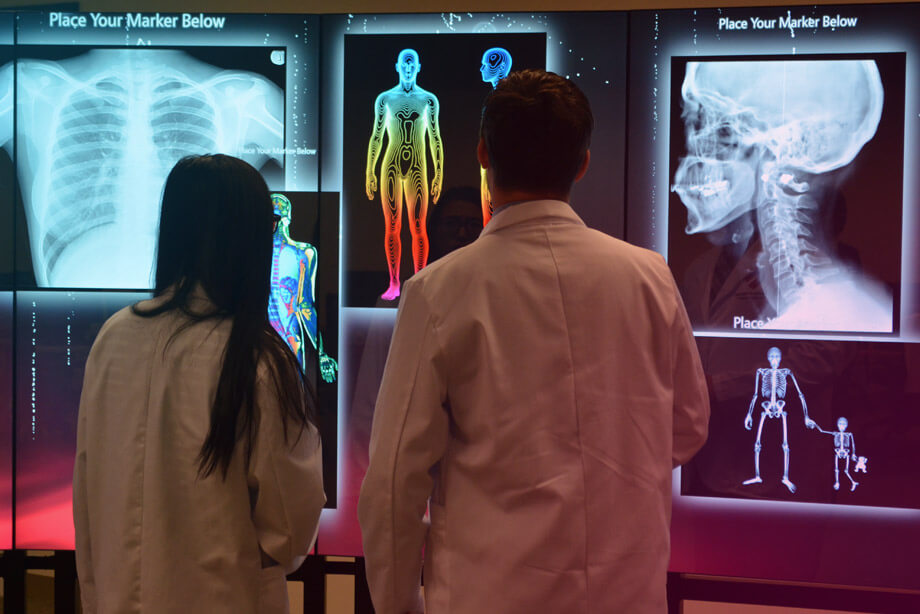
The MultiTaction iWall Helps Improve Outcomes
The MultiTaction iWall is very intuitive and a great first introduction to visualization and interacting with images. It literally gets students out of their seats and working together on projects.
The iWall is used to create a very realistic, hands-on, interactive, scenarios for students to learn and practise. It offers more than learning the “how-to” of a procedure. Up at the iWall, students learn how to relate and think through problems, and practise the critical thinking skills they will need under fire.
MULTITACTION IS AN IMPORTANT STEP IN THE JOURNEY INTO ADOPTING VISUALIZATION AND VIRTUAL REALITY.
While it is certainly important to understand theory, the iWall allows learners to put the theory into practice.
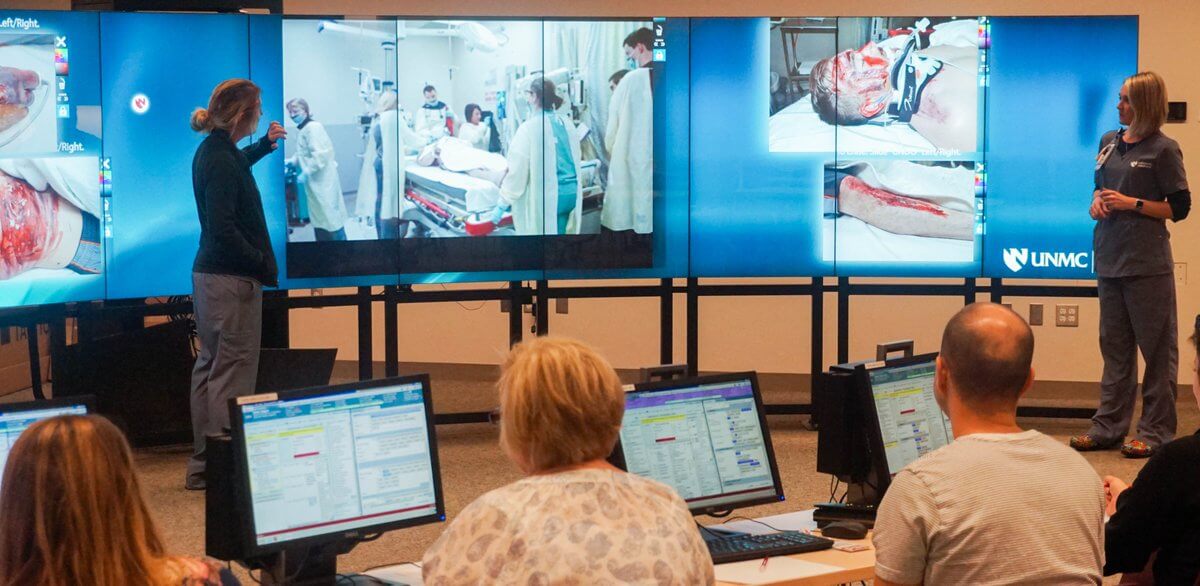
“Now we are in a position where virtually anything that can happen to a patient in the healthcare system can be realistically and accurately simulated.” Schmidt reports. Healthcare providers do not feel comfortable working for the first time on a real patient. They want to feel competent as well as develop confidence by using simulation before working in the real world of medicine.
Download the full case study to see how UNMC’s iEXCEL makes Nebraska the hub of some of the most revolutionary thinking in the world of medical education. Their mission to accelerate the adoption of modeling and simulation technology will reshape the way in which medical education is delivered.
You can download the full case study below



Leave a Reply